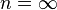Units: It is the measurement of Physical quantity.It is one of the important factor in Engineering
field.It is mainly classified into two units.
1)Fundamental units
2)Derived units
Fundamental units:
It is the base unit for all physical quantity.There are seven base units are kilogram,candela,metre,second,ampere,kelvin and mole.Most probably fundamental units are denoted as Length(L),Mass(M) and Time(t).
Derived units:
The units which is derived from the Fundamental units are called Derived units
e.g., Volume, area,velocity,pressure.
System of units:
There are four types of system of units,which are commonly used and universally
recognised.
1)C.G.S units
2)F.P.S units
3)M.K.S units
4)S.I. units
C.G.S units :
In this system,fundamental units of Length,mass,time are centimetre,gram and time.It is also known as absolute units(not depend on arbitrary units)
F.P.S units :
In this system,fundamental units of length,mass and time are foot,pound and second respectively.
M.K.S units:
In this system,fundamental units of length,mass and time are mass,kilogram and second respectively.It is also known as engineer's units.
International System of Units(S.I. units):
When Maxwell first introduced the concept of a coherent system, he identified three quantities that could be used as base units: mass, length and time. Giorgi later identified the need for an electrical base unit. Theoretically any one of electric current,potential difference, electrical resistance, electrical charge or a number of other quantities could have provided the base unit, with the remaining units then being defined by the laws of physics. In the event, the unit of electric current was chosen for SI. Another three base units (for temperature, substance and luminous intensity) were added later.It is the most widely used system of measurement.The seven base units are metre,kilogram,second,ampere,kelvin,mole and candela.
Important units:
SI Units and Symbols used in the Guide
Subject
|
Physical Quantity
|
Symbol
|
Name
|
Unit
|
Mechanics
|
Mass
|
m, M
|
kilogram
|
kg
|
Linear position
Length, Distance
Radius
|
x, r
l, d
R
|
meter
|
m
|
Time
|
t, 
|
second
|
s
|
Linear angle,
Angular position
|
 , , 
|
radian
|
rad
|
Spherical angle
|
|
steradian
|
sr
|
Area
|
A
|
-
|
m2
|
Volume
|
V
|
-
|
m3
|
Moment of inertia
|
I
|
-
|
kg*m2
|
Density
|
|
-
|
kg/m3
|
Linear velocity
|
v, u, c
|
-
|
m/s
|
Angular velocity
|
|
-
|
rad/s
|
Linear momentum
|
p
|
-
|
kg*m/s
|
Angular momentum
|
L
|
-
|
kg*m2/s
|
Linear acceleration
|
a
|
-
|
m/s2
|
Angular acceleration
|
|
-
|
rad/s2
|
Force
|
F
|
newton
|
N=kg*m/s2
|
Torque
|
|
-
|
N*m
|
Impulse
|
I
|
-
|
N*s
|
Work
Energy
|
W
E
|
joule
|
J=N*m
|
Power
|
P
|
watt
|
W=J/s
|
Dynamic viscosity
|
|
-
|
Pa*s
|
Electricity and Magnetism
|
Current
|
I
|
ampere
|
A
|
Charge
|
Q, q, e
|
coulomb
|
C=A*s
|
Current density
|
j
|
-
|
A/m2
|
Volume charge density
|
|
-
|
C/m3
|
Surface charge density
|
|
-
|
C/m2
|
Linear charge density
|
|
-
|
C/m
|
Electric potential
Voltage
emf
|
V
|
volt
|
V=J/C
|
Electric field
|
E
|
-
|
N/C, V/m
|
Electric flux
|
|
-
|
V*m
|
Electric moment
|
pe
|
-
|
C*m
|
Resistance
|
R, r
|
ohm
|
 =V/A
|
Specific resistance
|
|
-
|
 *m
|
Capacitance
|
C
|
farad
|
F=C/V
|
Specific conductivity
|
|
-
|
(  *m) -1 |
Magnetic field
|
B
|
tesla
|
T=N/(A*m)
|
Magnetic flux
|
|
weber
|
Wb=T*m2=V*s
|
Inductance
Mutual-inductance
|
L
M
|
henri
|
H=Wb/A
|
Magnetic moment
|
pm
|
-
|
A*m2
|
Polarization
|
P
|
-
|
C/m2
|
Magnetization
|
I
|
-
|
A/m
|
Thermodynamics
|
Temperature
|
T
|
kelvin
|
K
|
Substance quantity
|
M
|
mole
|
mol
|
Pressure
|
P
|
-
|
Pa
|
Heat
|
Q
|
-
|
J
|
Heat capacity
Entropy
|
C
S
|
-
|
J/K
|
Specific heat
|
c
|
-
|
J/(kg*K)
|
Molar heat
|
cm
|
-
|
J/(mol*K)
|
energy flux
|
j
|
-
|
W/m2
|
Surface tension
|
|
-
|
N/m
|
Stress
Elasticity modulus
|
E
|
pascal
|
Pa=N/m2
|
Oscillations and Waves
|
Wavelength
|
|
-
|
m
|
Wave number
|
k
|
-
|
m-1
|
Frequency
|
f
|
hertz
|
Hz
|
Energy density
|
|
-
|
J/m3
|
Energy flux
|
J
|
-
|
J/m2
|
Intensity
|
I
|
-
|
J/(m2*s)
|
Reactance
Impedance
|
X
Z
|
ohm
|
 =V/A
|
Optics
|
Focal length
|
f
|
-
|
m
|
Luminous intensity
|
I
|
candela
|
cd
|
Luminous flux
|
|
lumen
|
lm=cd*m2
|
Illuminance
|
E
|
lux
|
lk=lm/m2
|
Brightness
|
L
|
-
|
cd/m2
|
Linear absorption coefficient
|
|
-
|
m-1
|
Quantum Physics
|
Mass absorption coefficient
|
|
-
|
m2/kg
|
Radioactive activity
|
A
|
becquerel
|
Bq=s-1
|
Absorbed dose
|
D
|
gray
|
Gy=J/kg
|
|
(Most Important) Unit Conversions
- length
- area
- volume
- mass
- pressure
- energy
- power
- temperature
- radioactivity
- scientific notation
Length
- 1 (statute) mile (mi) = 1.6093 kilometer (km)
- 1 (nautical) mile (mi) = 1.8520 kilometer (km)
- 1 foot (ft) = 0.3048 meter (m)
- 1 yard = 0.9144 meter (m)
- 1 inch (in) = 2.54 centimeter (cm)
- 1 angstrom (A) = 10-8 centimeter (cm) = 10-10 meter (m)
Area
- 1 square kilometer (km2) = 106 square meters (m2) = 100 hectares (ha)
- 1 hectare (ha) = 10,000 square meters (m2)
- 1 acre (ac) = 4047 square meters (m2) = 0.4047 hectare (ha)
Volume
- 1 milliliter (ml) = 1 cubic centimeter (cm3)
- 1 cubic meter (m3) = 1000 liters (L)
- 1 (US) quart (qt) = 0.9461 liter (L)
- 1 (US) gallon (gal) = 3.7854 liter (L)
- 1 (US) pint = 0.4723 liter (L)
- 1 (US) fluid ounce = 29.6 milliliter (ml)
Mass
- 1 metric ton (m.t.) = 1000 kilograms (kg)
- 1 pound (lb) = 0.4535924 kilogram (kg)
- 1 ounce (oz) = 28.3495 grams (g)
Pressure
- 1 pascal (Pa) = 1 newton/square meter (N/m2) = 1 Kg m-1 s-2
- 1 bar = 0.98692 atmosphere (atm) = 105 pascals (Pa)
- 1 pound per square inch (psi) = 68.97 millibars (mb) = 6897 pascals (Pa)
Energy
- 1 joule (J) = 1 newton meter (Nm)
- 1 calorie (cal) = 4.184 joule (J)
- 1 kilowatt hour (kWh) = 3.6 x 106 joules (J) = 8.60 x 105 calories
Power (energy per unit time)
- 1 watt (W) = 1 joule per second (J/s) = 14.34 calories per minute (cal/min)
Temperature
- from Fahrenheit to Celsius: C = (F - 32) x 5/9
- from Celsius to Fahrenheit: F = (C x 9/5) + 32
- from Celsius to Kelvin: K = C + 273.15
Radioactivity
- 1 Curie (Ci) = 3.7x1010 Becquerel (Bq)
- 1 Gray (Gy) = 1 J/kg tissue = 100 rad
Commonly used prefixes...
Scientific notation
|
Prefix...........
|
Exponent
|
Examples of exponential usage:
|
|
peta (P)
|
15
|
amount of CO2 in atmosphere (as C)- 750 Pg (or Gt)
|
|
tera (T)
|
12
|
|
|
giga (G)
|
9
|
pool sizes: amount of water in ocean - 1.37 x 109 km3
|
|
mega (M)
|
6
|
rates: flow of Anatarctic Circumpolar Current - 200 x 106 m s-1
|
|
kilo (k)
|
3
|
distance New York - Albany ~ 350km
|
|
hecto (h)
|
2
|
atmospheric pressure: ~1012.5 hPa (=1012.5 mbar)
|
|
base unit
|
0
| |
|
milli (m)
|
-3
|
typical amount of medicine ~1ml
|
|
micro (m)
|
-6
| |
|
nano (n)
|
-9
|
wavelength of violet light ~400nm
|
|
pico (p)
|
-12
|
size of atom ~10pm
|
|
femto (f)
|
-15
|
detection limit of gas chromatographs for SF6 : ~1 fmole/L
|













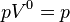
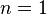
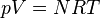
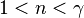

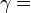
 is the isentropic exponent, yielding an isentropic process (adiabatic and reversible). It is also widely referred as adiabatic index, yielding an adiabatic process (no
is the isentropic exponent, yielding an isentropic process (adiabatic and reversible). It is also widely referred as adiabatic index, yielding an adiabatic process (no